[자료구조] Tree 01
April 11, 2021
#자료구조#algorithm#javascript
Tree
자료구조지만 복잡한 로직이 많이 들어감
트리 (Tree) 구조
트리: Node와 Branch를 이용해서, 사이클을 이루지 않도록 구성한 데이터 구조
사이클이 없는 이라는 것은, Siblings 끼리 연결되지 않는다는 것 (Sibilings 끼리 연결되면 Parents - Child - Siblings 사이에 사이클이 생기므로)
실제로 어디에 많이 사용되나?
트리 중 이진 트리(Binary Tree) 형태의 구조로, 탐색(검색) 알고리즘 구현을 위해 많이 사용됨
알아둘 용어
- Node: 트리에서 데이터를 저장하는 기본 요소 (데이터와 다른 연결된 노드에 대한 Branch 정보 포함)
- Root Node: 트리 맨 위에 있는 노드
- Level: 최상위 노드를 Level 0으로 했을 때, 하위 Branch로 연결된 노드의 깊이를 나타냄
- Parent Node: 어떤 노드의 다음 레벨에 연결된 노드
- Child Node: 어떤 노드의 상위 레벨에 연결된 노드
- Leaf Node (Terminal Node): Child Node가 하나도 없는 노드
- Sibling(Brother Node): 동일한 Parent Node를 가진 노드
- Depth: 트리에서 Node가 가질 수 있는 최대 Level
이진 트리와 이진 탐색 트리 (Bineary Search Tree)
- 이진 트리: 노드의 최대 Branch가 2인 트리
- 이진 탐색 트리(Binary Search Tree,BST): 이진 트리에 다음과 같은 추가적인 조건이 있는 트리
-
왼쪽 노드는 해당 노드보다 작은 값, 오른쪽 노드는 해당 노드보다 큰 값을 가지고 있음!

자료 구조 이진 탐색 트리(BST)의 장점과 주요 용도
- 주요 용도: 데이터 검색(탐색)
- 장점: 탐색 속도를 개선할 수 있음
이진트리와 정렬된 배열간의 탐색 비교
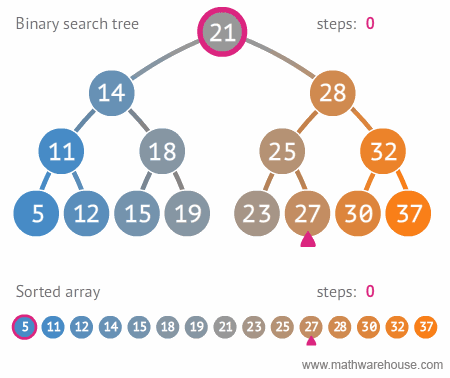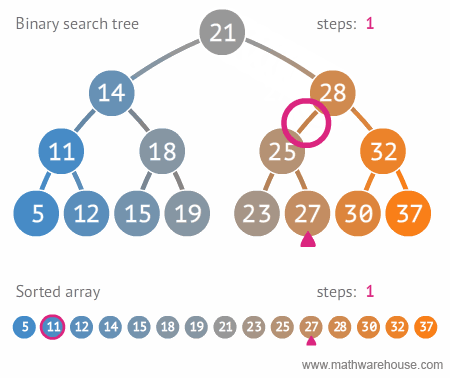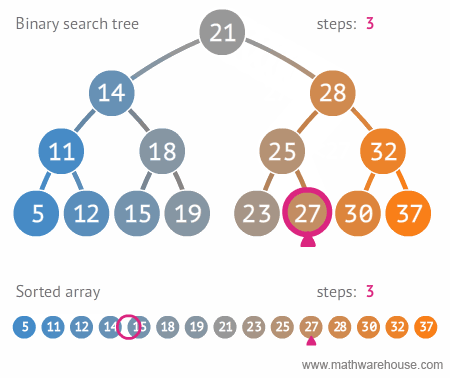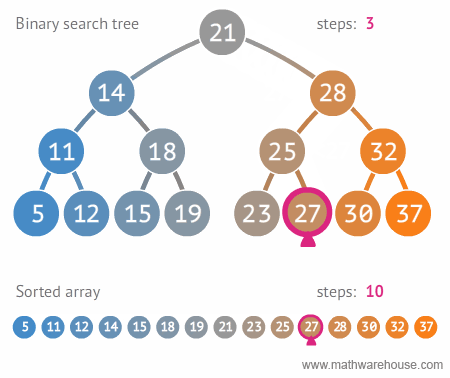
링크드 리스트를 활용해서 BST 구현
Node 구현
class Node {
value;
left;
right;
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}BST에 데이터 넣기
BST 조건에 부합하게 데이터를 넣어야 함
class NodeManagement {
head;
constructor(head) {
this.head = head;
}
insert(value) {
let currentNode = this.head;
while (true) {
if (value < currentNode.value) {
if (currentNode.left) {
currentNode = currentNode.left;
} else {
currentNode.left = new Node(value);
return;
}
} else {
if (currentNode.right) {
currentNode = currentNode.right;
} else {
currentNode.right = new Node(value);
return;
}
}
}
}
}
const head = new Node(3);
const BST = new NodeManagement(head);
BST.insert(1);
BST.insert(4);
console.log(BST);BST 탐색
class Node {
value;
left;
right;
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
class NodeManagement {
head;
constructor(head) {
this.head = head;
}
insert(value) {
let currentNode = this.head;
while (true) {
if (value < currentNode.value) {
if (currentNode.left) {
currentNode = currentNode.left;
} else {
currentNode.left = new Node(value);
return;
}
} else {
if (currentNode.right) {
currentNode = currentNode.right;
} else {
currentNode.right = new Node(value);
return;
}
}
}
}
search(value) {
let currentNode = this.head;
while (currentNode) {
if (currentNode.value === value) {
return currentNode;
} else {
currentNode =
currentNode.value > value ? currentNode.left : currentNode.right;
}
}
return null;
}
}
const head = new Node(3);
const BST = new NodeManagement(head);
BST.insert(1);
BST.insert(4);
BST.insert(5);
console.log(BST.search(4));